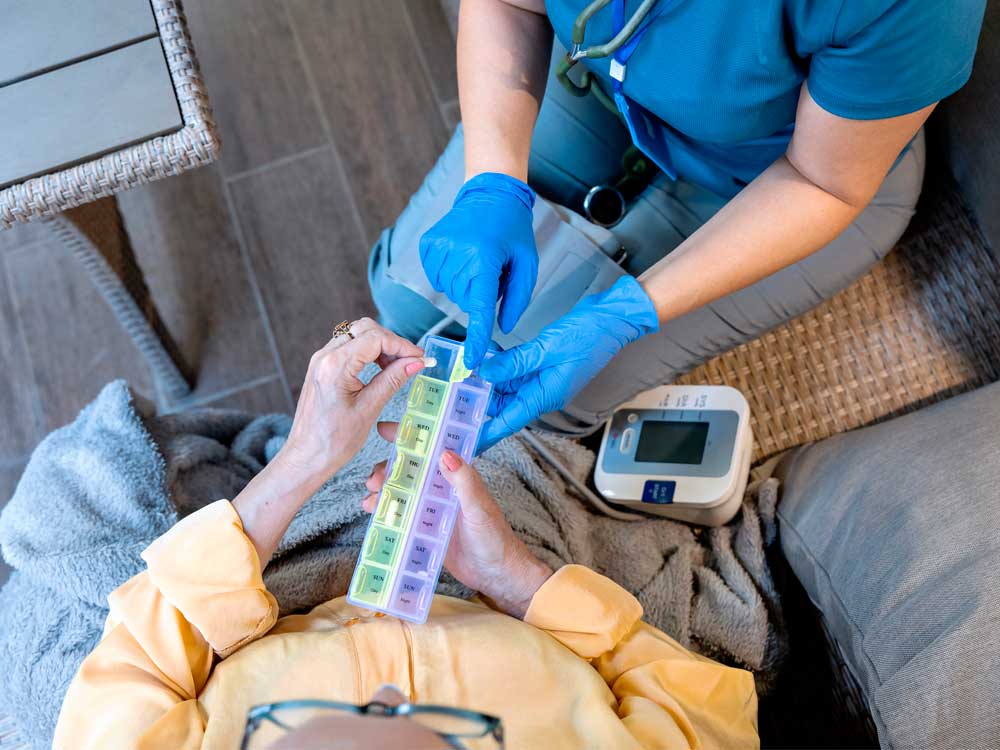
Proper medication management is essential for individuals with kidney disease, as the kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste and regulating various bodily functions. When kidney function declines, medications can build up in the body, increasing the risk of side effects and toxicity.
Understanding Kidney Function and Medications
The kidneys filter waste, balance fluids, and regulate electrolytes. Many medications are processed through the kidneys. Impaired kidney function can lead to:
- Reduced drug clearance, causing medications to stay in the body longer.
- Increased drug toxicity, leading to harmful side effects.
- Electrolyte imbalances, which can worsen kidney disease.
Patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) should work closely with their healthcare providers to adjust medications based on their kidney function, typically measured by the glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
Medications to Use with Caution
Certain medications require special attention in kidney disease and patients should work closely with the Nephrologist to ensure that the medications are ok to take.
A. Pain Relievers (NSAIDs and Opioids)
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen can reduce kidney blood flow and worsen kidney function.
- Opioids should be used cautiously, as their metabolism may be altered in kidney disease, increasing the risk of sedation and respiratory depression.
B. Blood Pressure Medications
- ACE inhibitors (e.g., lisinopril, enalapril) and ARBs (e.g., losartan, valsartan) protect the kidneys but can increase potassium levels. Regular monitoring is essential.
- Diuretics help control fluid retention but can affect electrolyte balance.
C. Antibiotics
- Many antibiotics, such as aminoglycosides (e.g., gentamicin) and vancomycin, are cleared by the kidneys and may require dose adjustments to prevent toxicity.
D. Diabetes Medications
- Metformin is commonly used for diabetes but can increase the risk of lactic acidosis in advanced kidney disease. It is typically avoided in severe CKD.
- Insulin and other diabetes medications may require dose adjustments as kidney function declines.
E. Over-the-Counter Supplements and Herbal Remedies
- Many herbal supplements, such as St. John’s Wort and licorice root, can interfere with kidney function or interact with prescribed medications. Always consult a healthcare provider before using any supplements.
Safe Medication Practices for Kidney Patients
To ensure medication safety, patients with kidney disease should follow these guidelines:
A. Complete regular medication reviews with your healthcare provider.
- Keep an updated list of all medications, including prescriptions, over-the-counter drugs, and supplements.
B. Avoid Nephrotoxic Medications
- Certain drugs, such as NSAIDs and some antibiotics, can damage the kidneys. Always check with a doctor before starting new medications.
C. Stay hydrated
- Proper hydration helps maintain kidney function and reduce the risk of medication buildup. However, in advanced CKD, fluid intake may need to be limited to prevent fluid overload.
E. Watch for side effects
- Symptoms such as nausea, confusion, swelling, or changes in urination may indicate medication-related kidney problems. Report any unusual symptoms to your nephrologist.
F. Use one Pharmacy
- Filling prescriptions at a single pharmacy allows pharmacists to check for drug interactions and ensure proper dosing.
Working with a Healthcare Team
Managing medications in kidney disease requires a team approach, including:
- Nephrologists for kidney-specific care.
- Primary care physicians for overall health management.
- Pharmacists for medication safety and interactions.
- Dietitians to help manage diet-related medication interactions, such as potassium and phosphorus levels.
Final Thoughts
Medication management is a critical part of maintaining health in kidney disease. Patients should be proactive in discussing medications with their healthcare providers, follow prescribed guidelines, and remain vigilant about potential side effects. By taking these steps, individuals with kidney disease can help protect their kidneys and improve their overall well-being. If you have kidney disease, always consult your doctor or pharmacist before making any changes to your medication routine.
Stay informed and take control of your kidney health!